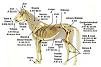
VITAMIN A
|
- EAR - Lowered resistance to infections.
- EYE - Xerophthalmia; night blindness; faulty vision; conjunctivitis.
- NOSE & THROAT - Infections of mucous membranes.
- TONGUE - Inflammations; glossitis.
- TEETH & GUMS - Aids in utilization of calcium; defective dentin; inflammation of gums.
- BLOOD VESSELS - By lowering of blood serum esterase, may affect fat metabolism. (see also Iron)
- NERVES - Degeneration of nervous system characterized by lack of co-ordination of legs and impairment of vision.
- HEART - Edema; lowered resistance to infections.
- HOOFS - Cracks, furrows, and abnormal growth.
- LUNGS- Lowered resistance to infections; haemorrhagic conditions.
- LIVER - Diseased conditions of organ may reduce capacity for storing vitamin A, and conversion of carotene and other pigment precursors in vitamin A.
- GASTRO-INTESTINAL SYSTEM - Disturbances in system may result in poor absorption of carotene and other pigment precursors of vitamin A, resulting in deficiency of this vitamin; poor gastric digestion.
- KIDNEYS - Nephritis; calculi; predisposes to secondary infections.
- COLON - Predisposition to oitis.
- URINARY BLADDER - Cystitis; calculi.
- SEXUAL ORGANS: Male - Deficiency of long standing may result in sterility; testicular degeneration, particularly when associated with deficiency of Vitamin E.
- SEXUAL ORGANS: Female - Sterility; weak or stillborn offspring; faulty lactation.
- MUSCLE - Lack of muscular co-ordination.
- SKIN & COAT - Predisposes to dermatitis of various types; roughened coat.
- BONES & JOINTS - Affects utilization of calcium, thereby affecting structure and formation of bones and joints; joint involvement with lameness and rarifying lesions in joint cartilages.
|
VITAMIN B1
|
- TONGUE - Glossitis; atrophy, edema.
- NERVES - Various disturbances associated with nervous system; nervousness; irritability; neuritis.
- BLOOD VESSELS - Capillary weakness; anemia.
- HEART - Decreased B content of heart muscle, normally high in the horse; myocardial infections; hypertrophy.
- GASTRO-INTESTINAL SYSTEM - Poor appetite; anorexia; gastric disturbances; faulty carbohydrate metabolism; nervous dyspepsia; inanition.
- COLON - Stasis; faulty absorption.
- SEXUAL ORGANS: Female - Termination of oestrus cycle; disturbances in endocrine secretions; faulty ovulation.
- URINARY BLADDER - Incontinence due to nervous irritability.
- MUSCLE - Muscular atrophy; degeneration and wasting of muscular fibre; vitamin not stored in muscle tissue, except cardiac muscle, to any appreciable extent.
- SKIN & COAT - Dry, scaly skin.
- BONES & JOINTS - Bone marrow degeneration.
|
VITAMIN B2
|
- EYE - Keratitis, corneal ulcer; cataracts.
- TONGUE - Ulcerations; oedema.
- NERVES - Nervous tissue involvement.
- TEETH & GUMS - Inflammation of gums.
- BLOOD VESSELS - Secondary anaemia.
- GASTRO-INTESTINAL SYSTEM - Faulty carbohydrate metabolism.
- COLON - Colitis; degenerative changes.
- SKIN & COAT - Certain types of dermatitis and skin lesions.
|
VITAMIN D3
|
- NERVES - Nervous irritability.
- TEETH & GUMS - Defective calcification; decay and dental caries. (see also Calcium & Phosphorus)
- BLOOD VESSELS - Deficiency of calcium and phosphorus in blood.
- SEXUAL ORGANS: Female - Affects reproduction and viability of offspring.
- MUSCLE - Rickets, resulting in poor muscle co-ordination.
- BONES & JOINTS - Poor absorption of calcium and phosphorus resulting in low content of theses mineral elements in the bones; poor dentition; rickets; osteomalacia and osteoporosis; faulty bone structure. (see also Calcium & Phosphorus)
|
VITAMIN B6
|
- NERVES - Loss of nerve and muscular co-ordination.
- GASTRO-INTESTINAL SYSTEM - Faulty metabolism.
- MUSCLE - Loss of muscular control.
- SKIN & COAT - Skin lesions; roughened coat.
|
NICOTINIC ACID
|
Nicotinic Acid & Other B Complex Factors
- TONGUE - Pellagra-like syndrome.
- BLOOD VESSELS - Anemia.
- GASTRO-INTESTINAL SYSTEM - Anorexia; digestive disturbances; poor assimilation.
- SKIN & COAT - Skin lesions; loss of hair.
|
VITAMIN E
|
- NERVES - Lack of nerve and muscular co-ordination.
- SEXUAL ORGANS: Male - Sterility, responding poorly to treatment; sterility associated with vitamin A responds more readily to vitamins A and E treatment; gonadal atrophy resulting in impotence.
- SEXUAL ORGANS: Female - Sterility, miscarriages; resorption of embryo; sexual frigidity.
|
CALCIUM
Bone-Building Element
|
Essential for building of normal bones and teeth.
- Also of importance in heart, nerve and muscle functions.
- Essential element in blood.
- Utilized by the body in enzyme activation.
- Essential for lactation and reproduction.
- Ratio of calcium to phosphorus intake of extreme importance; imbalance, particularly high phosphorus to calcium may result in osteodystrophia fibrosa.
Satisfactory ratio of Ca-P equals 1.0-0.8.
|
PHOSPHORUS
Bone-Building Element
|
Essential for building of sound bones and teeth.
- Also essential to metabolism of carbohydrates and fats and enzyme activation.
- Important in enzyme activity of vitamins B1 and B2.
- In form of its salts, acts as a buffer in blood and muscle tissue.
- Phosphorus may be deficient in the roughage feed in certain regions.
|
SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
Cell and Body Fluid Regulating Elements
|
Regulate osmotic pressure in cellular tissue of body fluids.
- Aid in regulation of buffer action of blood and ion balance.
- Potassium aids in regulating muscle function.
- Sodium protects body against excessive dehydration
- Deficiency of potassium not usually common in herbivorous animals who, however, require additional salt (sodium chloride) in their diets.
|
IRON
Blood-Building Element
|
Essential in formation of haemoglobin, in oxygen transfer, and in cell respiration.
- Aids in blood cell development and prevention of nutritional anaemia.
|
COPPER
Bio-Catalytic Element
|
Necessary together with iron in formation of haemoglobin, acting only as "Biological Catalyst".
- Aids in tissue respiration and prevention of certain types of nutritional anaemia.
|
MAGNESIUM
Muscle and Bone Building Element
|
Essential for normal growth of animals.
- Essential for nerve and muscle activity, and bone structure.
- Acts as a coenzyme in phosphorus metabolism.
|
MANGANESE
Essential Trace Element
|
- Essential for normal growth and the proper functioning of lactation and reproduction.
|
COBALT
Essential Trace Element
|
- Deficiency may result in loss of red blood cells and in emaciation and general rundown condition.
|
ZINC
Essential Trace Element
|
Aids in promotion of normal growth and tissue respiration.
- Interrelated with insulin and vitamin B1 deficiencies in certain animal species.
- May play role in development of normal coat of hair.
|
IODINE
Essential Trace Element
|
Essential in the growth and functions of the thyroid gland and formation of thyroxine.
- Important in regulation of basal metabolism.
- For prevention of goiter.
|